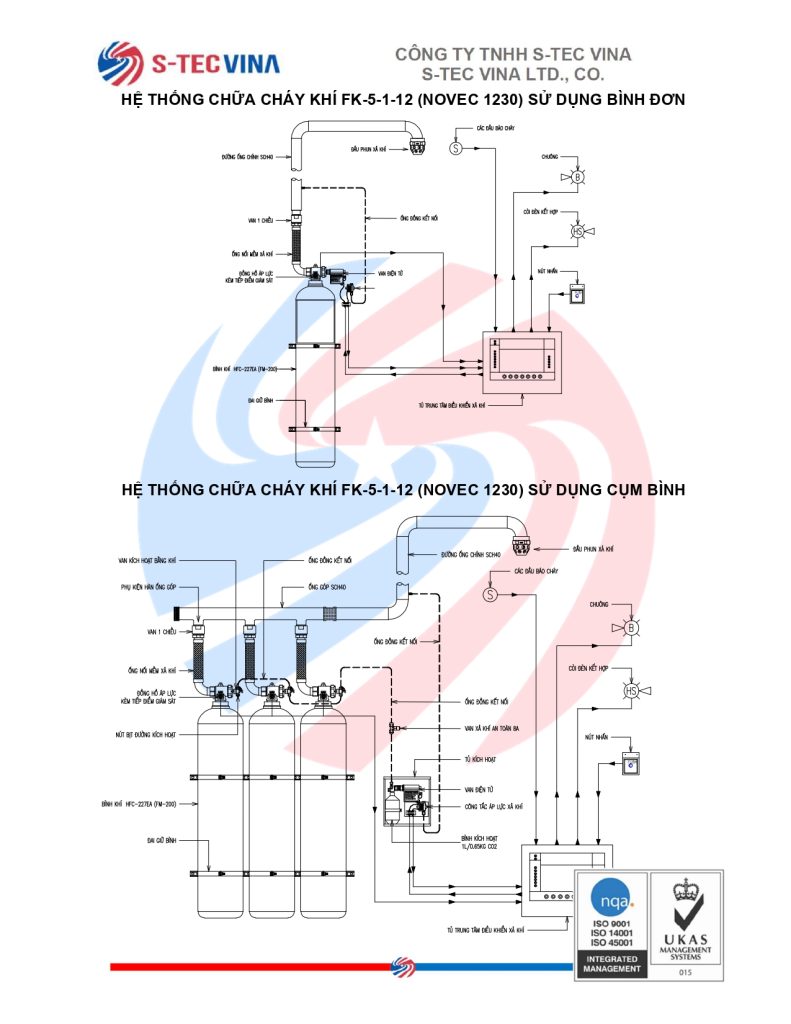
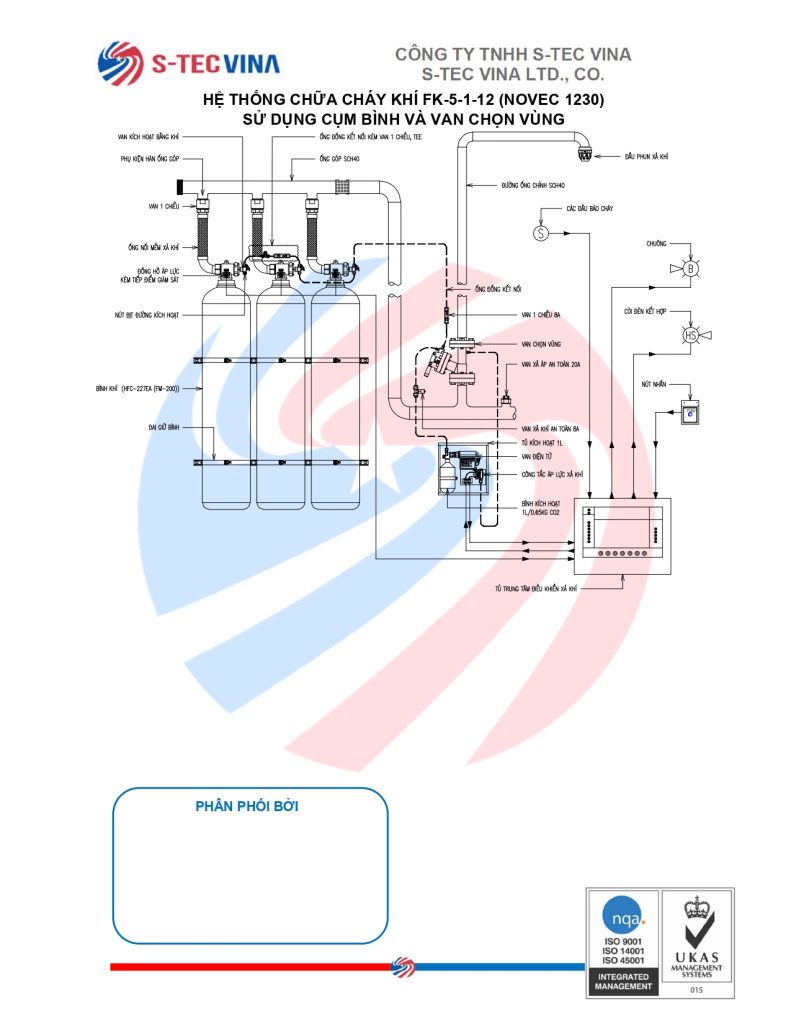
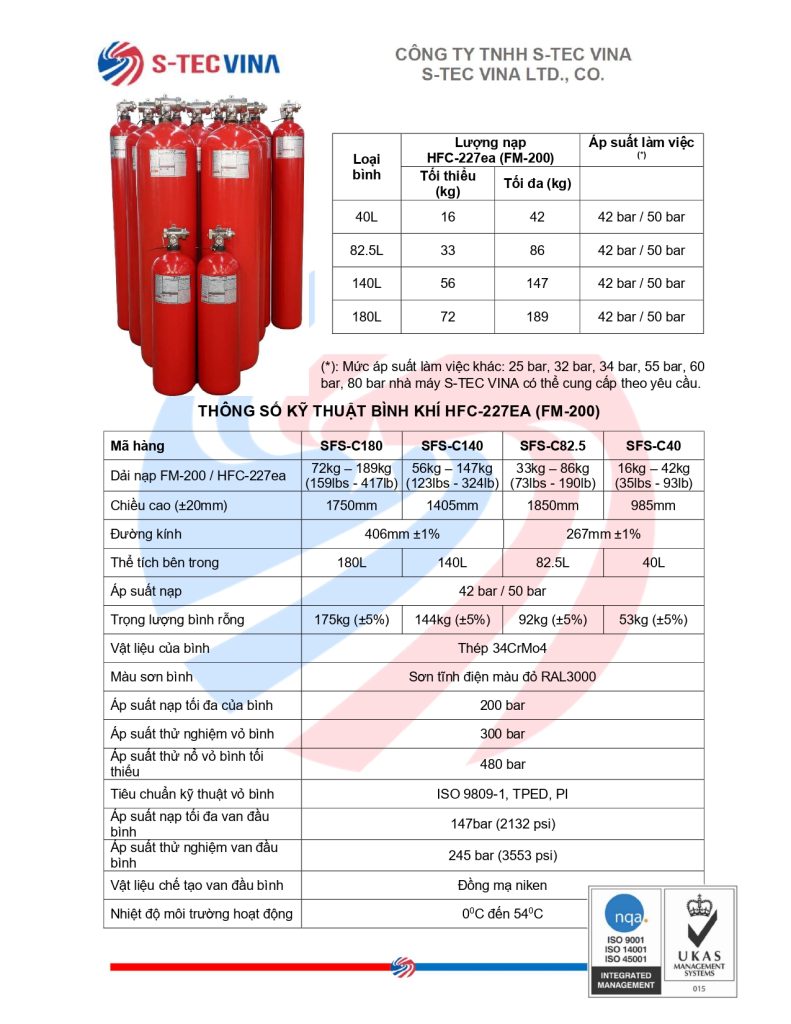
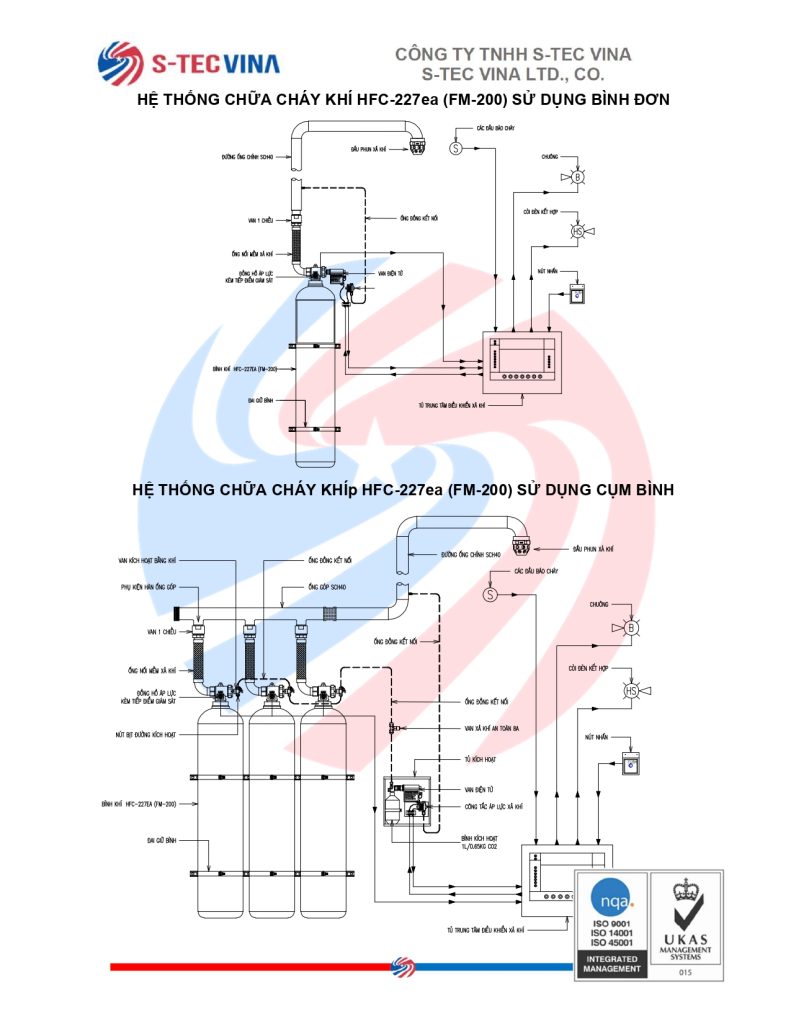
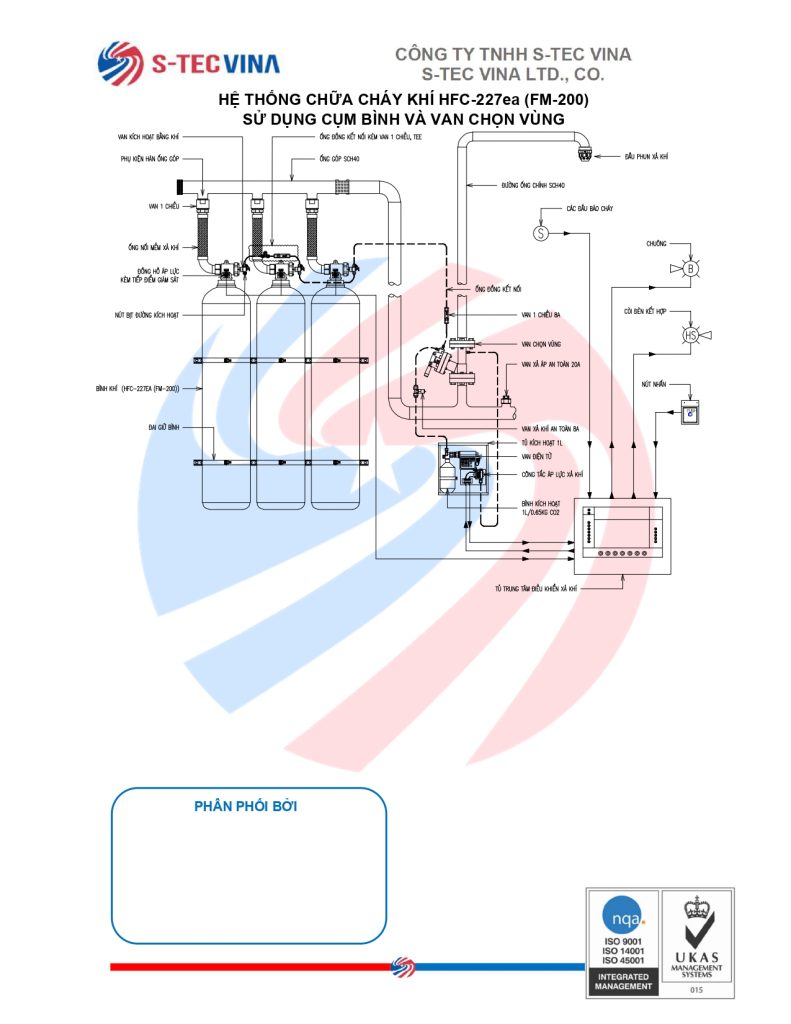
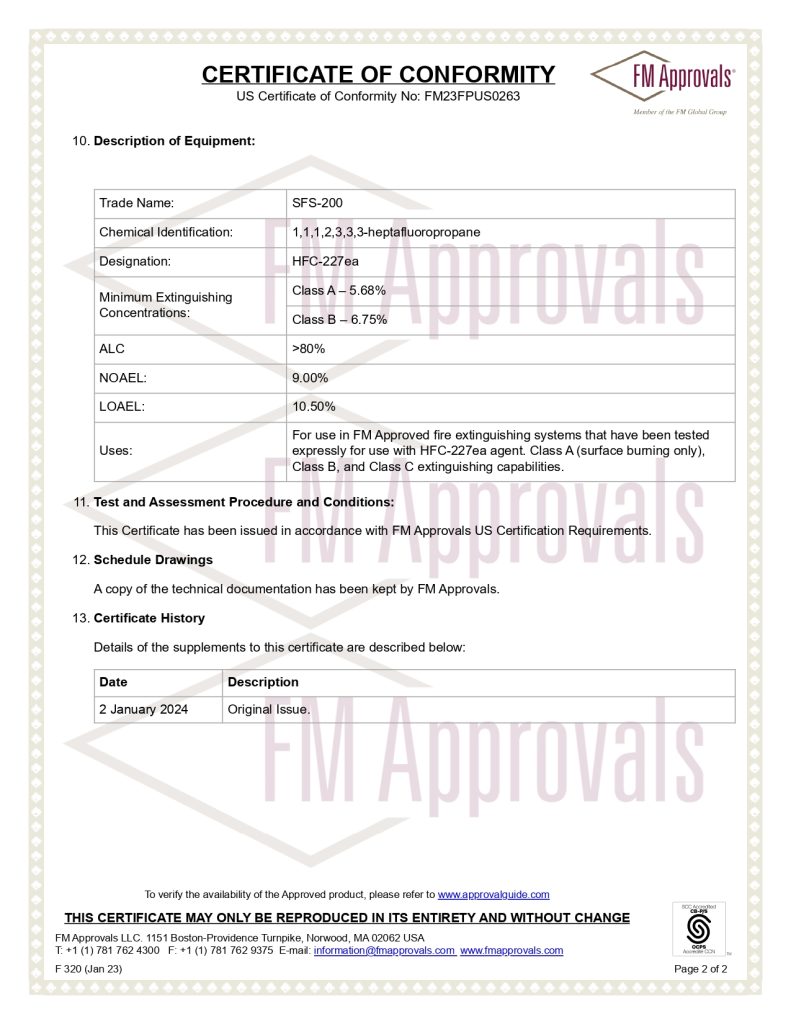
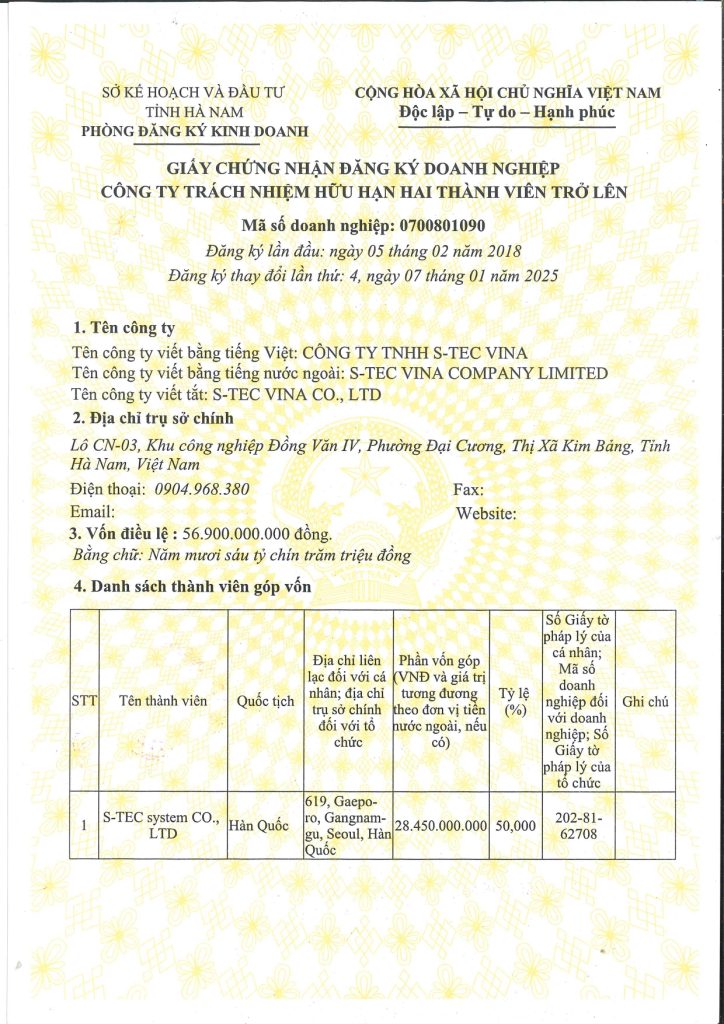
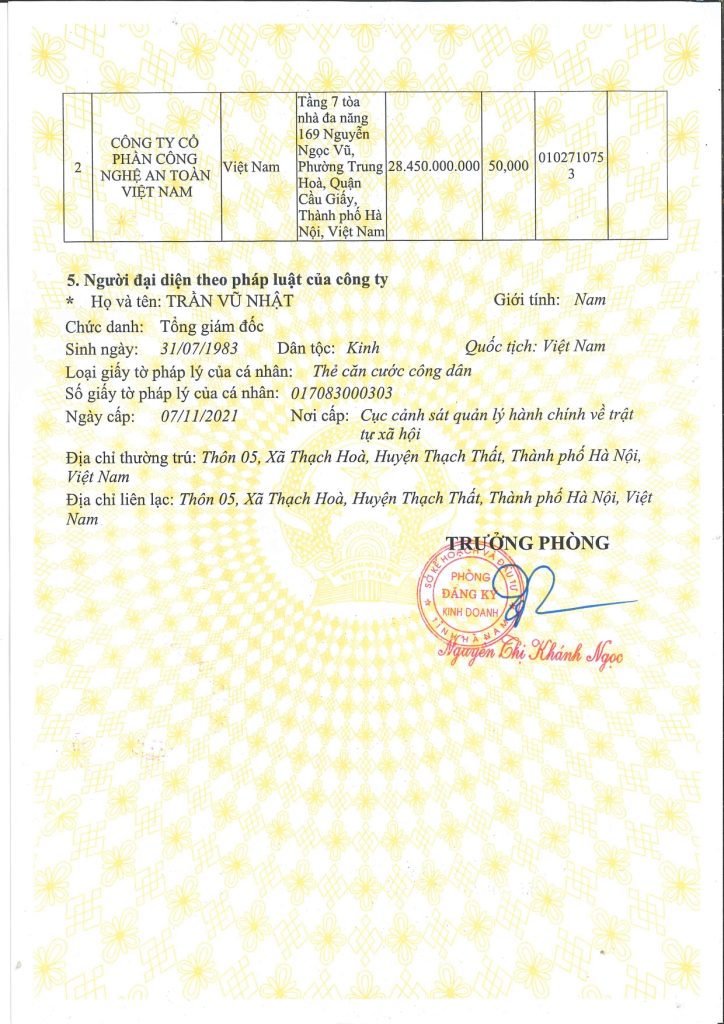
Sáng ngày 29 tháng 11, Quốc hội đã thông qua Luật Phòng cháy, chữa cháy và Cứu nạn, cứu hộ, cắt giảm và đơn giản hóa thủ tục hành chính, điều kiện đầu tư, sản xuất và kinh doanh cho người dân và doanh nghiệp.
So với luật hiện hành, số lượng thủ tục hành chính trong lĩnh vực phòng cháy, chữa cháy đã được giảm từ 37 xuống còn 10. Trong đó có hai thủ tục thẩm định thiết kế phòng cháy, chữa cháy; hai thủ tục kiểm tra nghiệm thu công trình; và sáu thủ tục cấp và cấp lại chứng chỉ đào tạo phòng cháy, chữa cháy.
Ban soạn thảo đã bỏ các quy định liên quan đến thẩm định thiết kế để giảm bớt các bước trung gian, tạo thuận lợi và minh bạch hơn cho người dân và doanh nghiệp; bỏ quy định dịch vụ phòng cháy, chữa cháy là ngành nghề đầu tư kinh doanh có điều kiện. Điều này giúp thúc đẩy xã hội hóa công tác phòng cháy, chữa cháy, tạo điều kiện thuận lợi hơn cho các cơ sở và doanh nghiệp trong việc tư vấn, thiết kế, thi công, sản xuất, nhập khẩu và kinh doanh phương tiện và thiết bị phòng cháy, chữa cháy.
Điều 20 quy định về phòng cháy cho nhà ở, trong đó nhà ở tại các thành phố trực thuộc trung ương, ở những khu vực không đảm bảo cơ sở hạ tầng giao thông, nguồn nước cho chữa cháy và các tiêu chuẩn kỹ thuật trong hoạt động phòng cháy, chữa cháy, phải đảm bảo một số điều kiện nhất định.
Cụ thể, nhà ở phải được trang bị bình chữa cháy; thiết bị truyền tín hiệu báo cháy kết nối với hệ thống cơ sở dữ liệu về cứu hộ, cứu nạn và truyền tín hiệu báo cháy. Ủy ban Nhân dân các thành phố trực thuộc trung ương xác định khu vực này và thực hiện theo lộ trình do Chính phủ quy định. Hiện nay, cả nước có 5 thành phố trực thuộc trung ương, bao gồm Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng và Cần Thơ.
Đối với nhà ở ở các khu vực khác, việc lắp đặt thiết bị báo cháy không bắt buộc, nhưng được khuyến khích. Ngoài ra, nhà ở phải có bếp an toàn, nơi thờ cúng, nơi đốt vàng mã; không để các vật dụng, chất dễ cháy hoặc nổ gần nguồn lửa hoặc nhiệt; có trang bị phòng cháy, chữa cháy phù hợp với khả năng; và sắp xếp lối thoát hiểm và cửa thoát hiểm.

Ủy ban Thường vụ Quốc hội cho rằng, nhà ở phải được trang bị thiết bị báo cháy là những nhà ở tại các khu vực đô thị có mật độ dân cư rất cao, đông đúc, nằm trong hẻm, ngõ sâu, và không có cơ sở hạ tầng giao thông hoặc nguồn nước đảm bảo cho chữa cháy.
Nhà ở trong nhóm này chủ yếu nằm ở các thành phố lớn (thành phố trực thuộc trung ương) và do lịch sử quy hoạch, xây dựng trước đây. Để đảm bảo việc triển khai kịp thời lực lượng và phương tiện chữa cháy, việc truyền tải thông tin nhanh chóng và báo cháy tới lực lượng Cảnh sát Phòng cháy chữa cháy là rất quan trọng.
Kế hoạch cung cấp nước phục vụ chữa cháy phải tận dụng “5 phút vàng” ban đầu khi đám cháy chưa bùng phát, để bảo vệ tính mạng và tài sản của người dân. Thiết bị truyền tín hiệu báo cháy là một thiết bị kỹ thuật tích hợp, kết nối với hệ thống cơ sở dữ liệu của các cơ quan chức năng.
Trong điều kiện kinh tế – xã hội hiện nay, việc lắp đặt thiết bị báo cháy phải được thực hiện theo lộ trình, đảm bảo phù hợp với quy mô và tính chất nguy cơ cháy nổ của từng loại cơ sở và địa phương. Do đó, luật không yêu cầu tất cả các tòa nhà phải có thiết bị báo cháy.
Đối với nhà ở kết hợp sản xuất và kinh doanh, luật mới quy định phải đảm bảo tất cả các điều kiện như đối với nhà ở bình thường, với khu vực sản xuất và kinh doanh hàng hóa có nguy cơ cháy nổ phải được tách biệt với khu vực sinh hoạt; phải có thiết bị báo cháy, giải pháp thông gió, và thiết bị phát hiện rò rỉ khí dễ cháy và nổ nguy hiểm.
Bên cạnh những nội dung trên, dự thảo luật còn quy định các điều kiện phòng cháy cho các cơ sở sản xuất và kinh doanh; đối với phương tiện; lực lượng chuyên môn và lực lượng huy động trong các tình huống phòng cháy và cứu hộ.
Nhà nước quyết định quyền khai thác khoáng sản chiến lược
Sáng cùng ngày, Quốc hội đã thông qua Luật Địa chất và Khoáng sản, quy định Nhà nước có trách nhiệm đầu tư và tổ chức khảo sát khoáng sản chiến lược; quyết định không đấu giá quyền khai thác khoáng sản đối với một số khu vực có khoáng sản chiến lược và quan trọng; và cho phép khảo sát và khai thác khoáng sản chiến lược theo thỏa thuận được quy định trong hiệp định liên chính phủ.
Khoáng sản chiến lược và quan trọng là các khoáng sản thiết yếu phục vụ phát triển kinh tế – xã hội bền vững và tăng cường quốc phòng, an ninh. Chiến lược địa chất, khoáng sản và công nghiệp khai thác đến năm 2030, với tầm nhìn đến năm 2045, nêu rõ khoáng sản chiến lược và quan trọng bao gồm đất hiếm, khoáng sản phóng xạ, kim loại quý, kim loại thiếu (vàng, thiếc – vonfram, đồng, niken), khoáng sản công nghiệp, khoáng sản sử dụng làm vật liệu xây dựng và khoáng sản thay thế cát sông, sỏi.
Khoáng sản chiến lược và quan trọng có đặc điểm là giá trị kinh tế cao và nhu cầu toàn cầu lớn. Chúng thường có sẵn hạn chế và việc khai thác rất phức tạp. Nhiều khoáng sản trong nhóm này là thành phần thiết yếu của sản xuất công nghệ cao như pin lithium-ion, vi mạch và năng lượng tái tạo.
Các địa phương có khoáng sản được khai thác sẽ nhận một phần lợi nhuận từ hoạt động này để đầu tư vào phát triển kinh tế – xã hội, theo quy định của pháp luật về ngân sách nhà nước. Người dân địa phương cũng được ưu tiên trong việc tuyển dụng cho các vị trí trong các dự án khai thác khoáng sản.
Hội đồng Nhân dân tỉnh có quyền quyết định mức đóng góp của các doanh nghiệp khai thác khoáng sản vào việc đầu tư hạ tầng và bảo vệ môi trường. Các doanh nghiệp này cũng có trách nhiệm đào tạo công nhân, hỗ trợ người dân bị ảnh hưởng bởi dự án và bồi thường thiệt hại. Khi dự án kết thúc, các doanh nghiệp phải chịu trách nhiệm đóng cửa mỏ và phục hồi môi trường.
Theo VNExpress